Hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) is required for β-cell survival in Type 1 diabetes (T1D) caused by immunological insults (#99)
Background: Our previous studies show that HIF-1α is important for β-cell survival and function in islet-transplantation but however; its significance in T1D is unknown.
Aim: To determine the role of HIF-1α in T1D onset caused by insults such as coxsackieviruses (CV), multiple low-dose streptozotocin (MLDS) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β).
Methods: NOD mice with β-cell-specific HIF-1α deletion (βHIF-1α) and floxed-controls were studied. For CV, mice were inoculated with 105 pfu of CVB4 or CVB1. Days 7 (peak), 21 (clearance) post-infection (dpi) and long-term were assessed. For MLDS, mice received 20mg/kg streptozotocin on days 1 to 5. For IL-1β, human islets from healthy donors and mouse islets were treated ± 10 pg/mL for 1, 2 or 24-hours.
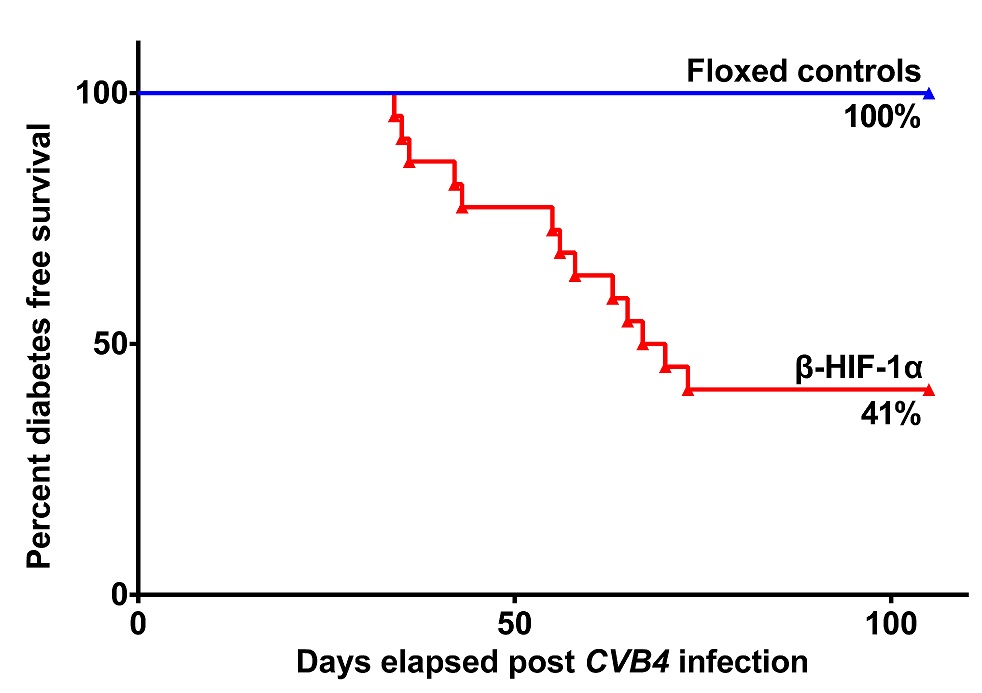
Results: At 7dpi, CVB4 infected βHIF-1α mice had higher pancreatic viral-load and elevated islet-infiltrates that constituted of higher percentages of CD3+ T-cells (p=0.0095) and CD19+ B-cells (p=0.019). By 21dpi virus was cleared. In the long-term study, florid-T1D developed in 13/22 βHIF-1α mice (59%), versus 0/11 of controls (0%, p≤0.001) by 32 weeks. Adoptive-transfer studies confirmed T1D, with 100% of NOD-SCID recipients of diabetic βHIF-1α splenocytes developing T1D. In ongoing studies, CVB1 induced florid-T1D in 4/9 β-HIF-1α mice (44%), versus 0/5 of controls (0%, p≤0.0001) by 11 weeks. When exposed to CVB4 orally by gavage, 3/6 β-HIF-1α mice (50%) thus far have developed florid-T1D versus 0/5 controls (0%). Following MLDS, βHIF-1α mice had increased BGLs, glucose intolerance by 1 week, and 8/8 mice (100%) developed florid-T1D versus 5/15 mice for controls (33%, p=0.0015). Human islets treated with IL-1β showed increased expression of pro-apoptotic markers BAX (1.7 fold, p≤0.01) and BAK1 (2.9 fold, p≤0.01) after 24-hours, versus controls. βHIF-1α mouse islets showed decreased expression of anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-xl (3.9 fold, p≤0.0001) and β-cell survival gene Pdx1 (11.1 fold, p≤0.0001) after 2-hours, versus control islets.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that β-cell HIF-1α is a common-regulator of β-cell susceptibility to T1D. This has important implications for the role of β-cells in T1D-development and suggests that increasing β-cell HIF-1α may protect against T1D development.